Danny Lee

Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a high energy molecule considered the energy currency for all species. Our laboratory has discovered that bacteria release ATP into culture medium, a novel phenomenon (Mempin et al., 2013). However, it isnt yet understood why this occurs. We hypothesize that extracellular ATP is needed for the conversion of D-amino acids and their incorporation into the cell wall, allowing bacteria to survive changing environmental conditions. Danny will investigate the role of ATP in D-amino acid metabolism and cell wall remodeling by measuring ATP release of cultures supplemented […]
Xinyi Zhang

Parkinsons disease is the second-most common neurodegenerative disorder, which currently has no effective treatment. The development of treatments can benefit from better understandings of how the neurodegeneration propagates in the brain. The most crucial contributor to the propagation is believed to be the transmission between neurons of the pathological protein, -synuclein. To study the unresolved transmission mechanism, Xinyi proposes an RNA-Seq study on neuronal models to measure the transient responses of cells exposed to -syn over time. RNA-Sequencing is a powerful tool for unbiased investigation of the highly coordinated responses […]
Lucian DiPeso

Pyroptosis is a poorly understood mode of cell suicide, one that functions as an alarm bell for the bodys immune system in response to infection. Though beneficial when properly regulated, the rapid immune response triggered by pyroptosis can, itself, produce disease and dysfunction. Pyroptosis has been identified as a possible contributor to cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and some neurodegenerative disorders. Understanding pyroptosis, then, could lead to novel treatments for a variety of human diseases. Unfortunately, despite ten years of research, uncovering how it precisely works has proven to be […]
Jehan Yang
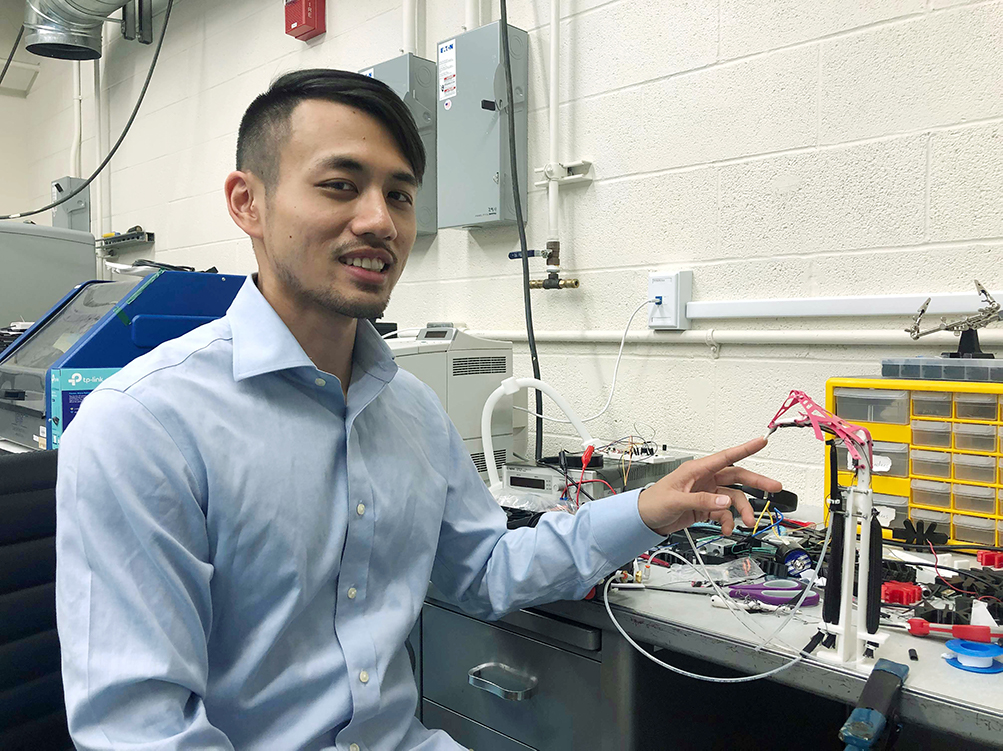
Utilizing 27 degrees of freedom, the human hand is a complex manipulator capable of tasks ranging from fingerstyle guitar to precise surgery. To replicate the human hand would produce a highly versatile tool in robotics and prostheses. Robots in the future might perform surgery while arm amputees could perform as well as anyone in sports and arts. Current hand replications have limitations of high expense and weight, with trade-offs in precision. For his project, Jehan aims to create an inexpensive and light manipulator, with improvements for precise control. He will […]
Victor Chen
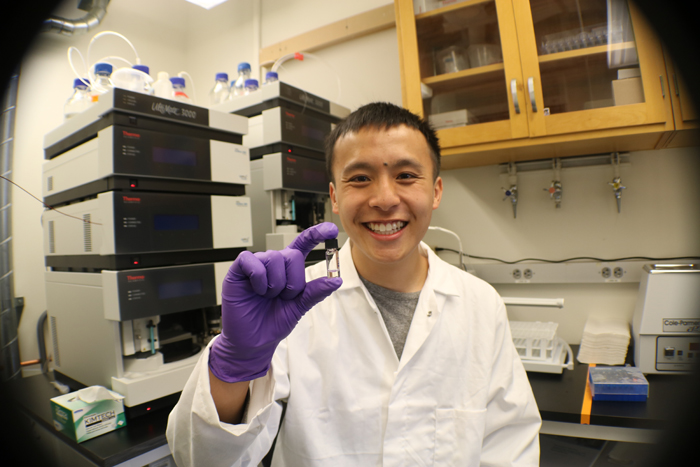
Actinomycetes, filamentous soil bacteria, have been the single richest source of medicinally relevant natural products, whose applications include anticancer agents, antifungal agents and antibiotics. However, actinomycetes still hold great potential for novel metabolite discovery. This is because the way they are typically grown in the laboratory fails to mimic cues in their natural environments that potentially induce the synthesis of novel metabolites. During this project, Victor will place actinomycetes in ecologically relevant contexts by reintroducing them to bacteria they would naturally encounter, in binary interactions, and subsequently analyze the metabolites […]
Daniel Quintana
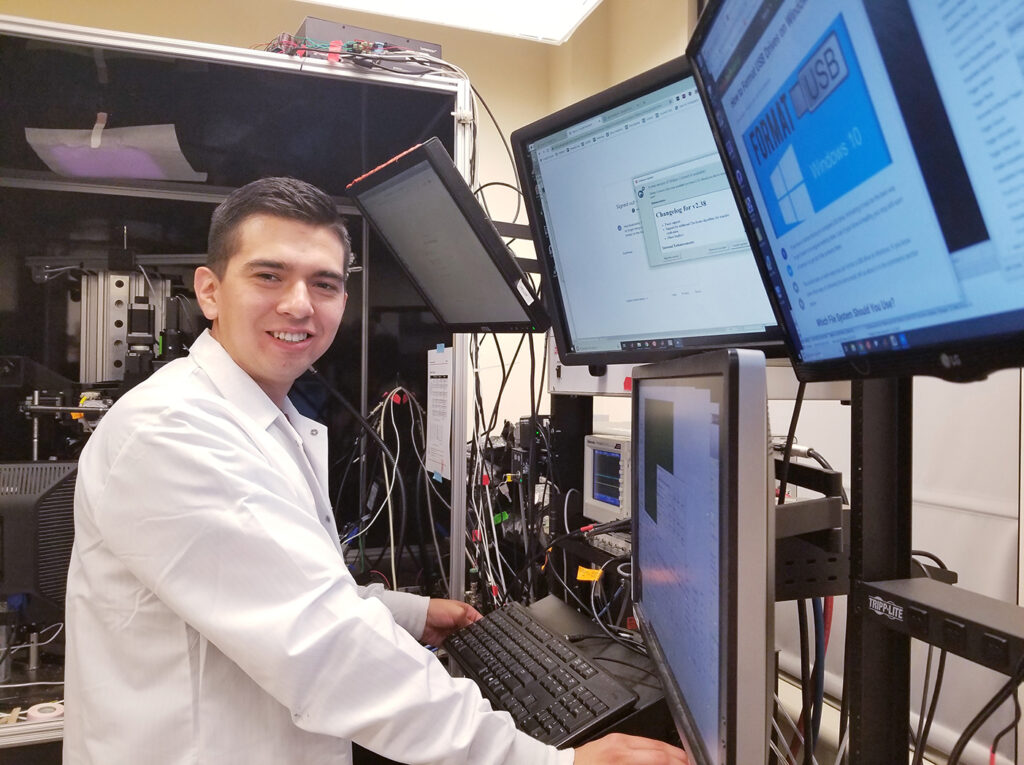

In mammals, detecting weak stimuli is crucial for animal survival. One way they could detect weak stimuli is spatial integration, pooling together weak signals over an area of visual space to strengthen the signal. In the cortex, vasointestinal peptide (VIP) cells are a group of interneurons that have a central role in pyramidal cell tuning and response modulation of other interneurons. However, the mechanisms behind how signals from different inhibitory interneurons affect the codification of sensory stimuli into percepts remains unclear. He will optogenetically activate and inhibit VIP interneurons in […]
Justin Baik
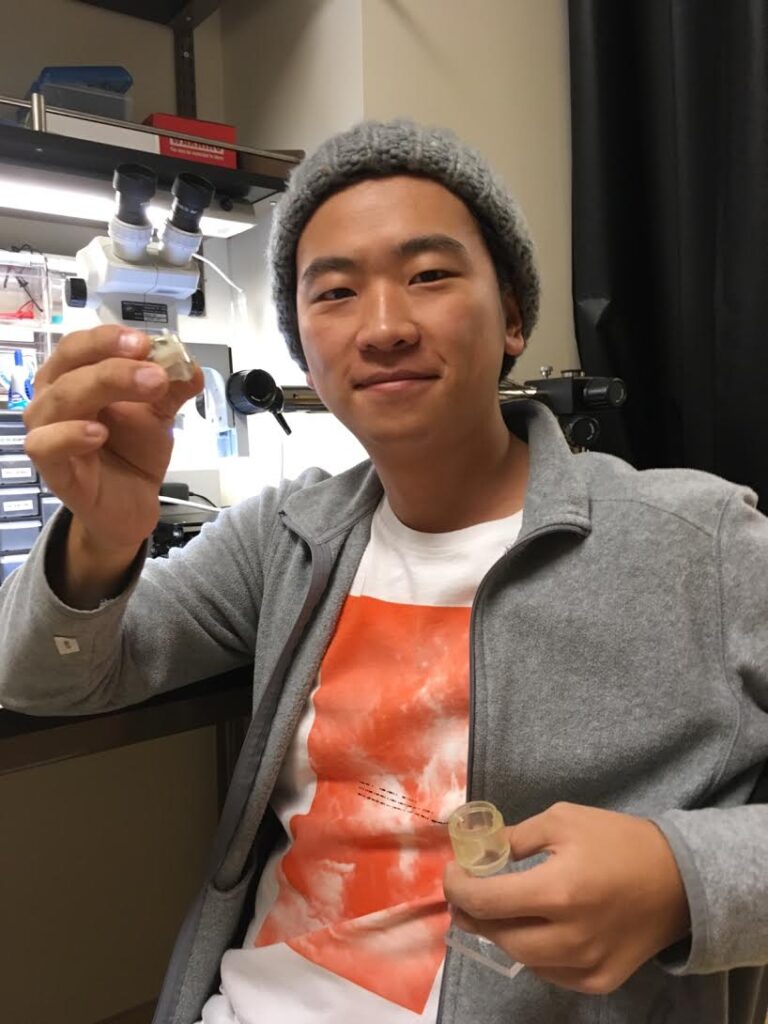

How does the brain convert sensory information to help us navigate around space? Spatial learning is what Justin believes to be the key in building the bridge between sensory input and navigation. The striatum, a region of the mammalian brain known to be crucial for spatial learning, will be deeply examined using the methods of optogenetics. In his project, Justin will be building methods to optically control striatal regions of freely behaving bats, and examine the neural circuitry that allows their sophisticated navigation around complex environments to be made possible. […]